Original Research Paper
Ricardo Hernández Pérez; René Salgado Delgado; Alfredo Olarte Paredes; Areli Marlen Salgado Delgado; Beatriz Flores Abarca; Oswaldo E. Silva Astudillo
Abstract
Rice husk (Oryza sativa L.) is considered an agroindustrial waste that requires alternative treatment to prevent it from becoming an environmental contaminant. Some recent reports have been able to produce Nanocellulose (CNCs) with this biomass, although with low yields, after using a complex of endo ...
Read More
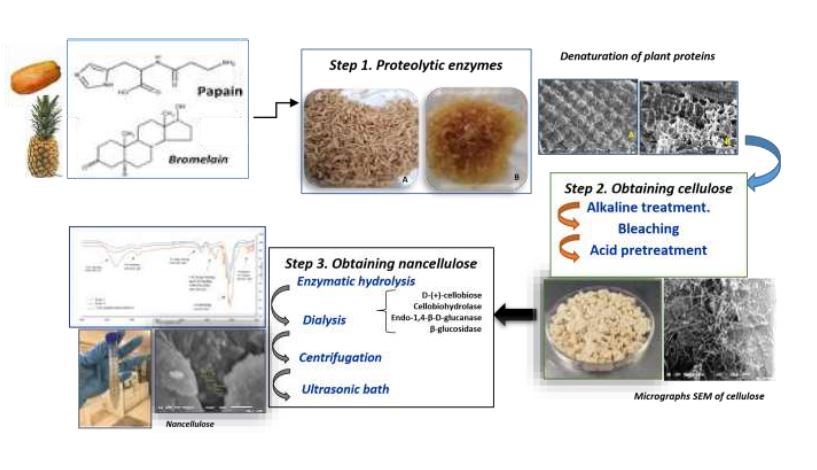
Rice husk (Oryza sativa L.) is considered an agroindustrial waste that requires alternative treatment to prevent it from becoming an environmental contaminant. Some recent reports have been able to produce Nanocellulose (CNCs) with this biomass, although with low yields, after using a complex of endo and exoenzymes. Work aimed to evaluate the previous effect of natural proteolytic enzymes (Bromelain/Papain) to degrade the fibrous structure of rice husk before obtaining Cellulose and for whitening, an alternative with hydrogen peroxide. In combination with subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis the new complex formed by four reagents: D-(+)-Cellobiose, endo-1,4-ꞵ-D glucanase, ꞵ-glucosidase, and Cellobiohydrolase, for the synthesis of Nanocrystals (CNCs). Satisfactory results indicated that it was possible to soften and modify the plant tissue structure, which allowed a final cellulose yield of 56.35%. The hydrolysis with the enzyme complex applied to Cellulose, achieved the obtaining of CNCs between 200-595 nm, after using the four enzymes in complex, with better results when used in a single phase, achieving a final yield of 1.8 -4.2% nanocellulose with process optimization.
google is broken
Original Research Paper
maryam Fayazi
Abstract
In the present study, different morphologies (viz., spherical and nanoroad) of zinc oxide (ZnO) were successfully deposited on the biochar support material via a simple hydrothermal approach. The biochar utilized in this research was obtained through the pyrolysis process of pistachio residues. Characterization ...
Read More
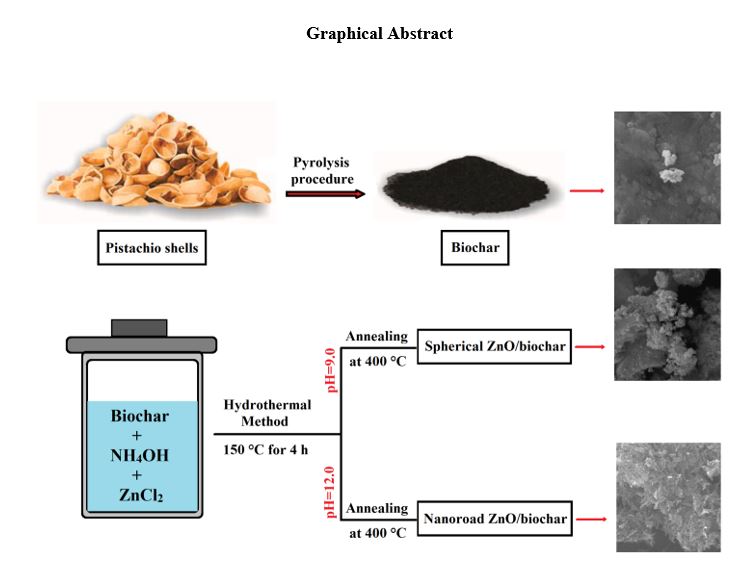
In the present study, different morphologies (viz., spherical and nanoroad) of zinc oxide (ZnO) were successfully deposited on the biochar support material via a simple hydrothermal approach. The biochar utilized in this research was obtained through the pyrolysis process of pistachio residues. Characterization of the prepared ZnO/biochr nanocomposites was carried out using FT-IR, XRD, DRS, EDS and SEM analyses. DRS data analysis revealed that the band gap energies of the fabricated nanocomposites were measured to be 2.98 eV and 3.08 eV for the spherical ZnO/biochar and nanoroad ZnO/biochar, respectively. Under visible light irradiations, the prepared photocatalysts were assessed for their photocatalytic abilities in degradation of methylene blue (MB) dye. The degradation of MB on ZnO/biochar catalysts demonstrates a strong correlation with a pseudo-first-order kinetic model. Besides, the suggested photocatalyst substance indicated good reusability, retaining its performance for at least five cycles. The utilization of low expense biochar support in conjunction with nanosized ZnO nanostructures presents a promising idea to achieve efficient photocatalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants.
فوتوکاتالیست ها
Original Research Paper
Ghasem Zolfaghari
Abstract
At present study, the removal of p-nitrophenol (PNP) by a newly designed mesoporous organocarbon, monolayers of ß-cyclodextrine (CD) on oxidzed ordered nanoporous carbon (OX-ONC) via 1,4-phenylene diisocyanate (PDI) linking denoted as CD-ONC was optimized. Furthermore, Au-doped mesoporous carbon ...
Read More
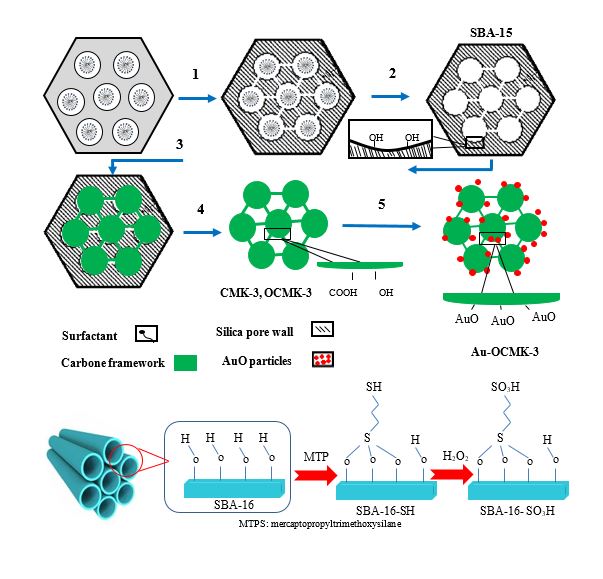
At present study, the removal of p-nitrophenol (PNP) by a newly designed mesoporous organocarbon, monolayers of ß-cyclodextrine (CD) on oxidzed ordered nanoporous carbon (OX-ONC) via 1,4-phenylene diisocyanate (PDI) linking denoted as CD-ONC was optimized. Furthermore, Au-doped mesoporous carbon CMK-3 denoted as Au-OCMK-3 was synthesized by using SBA-15. Au-OCMK-3 has been studied for removal of dibenzothiphene (DBT) and carbazole (CA) from n-hexane. Also the functionalization of SBA-16 mesoporous with sulfonic acid for arsenic (As (V)) and copper (Cu (II)) removal were carried out (SBA-16-SO3H). Maximum absorption capacity of CD-ONC was 100 mg/g. Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm was applied to describe the nature of PNP uptake and it was found that it occurred physically (E = 0.07 KJ/mol, CD-ONC). Value for Temkin’s heat of adsorption is positive for PNP (157.87 J/mol, CD-ONC). There are two physisorption models of PNP with the surface C=O groups of ONC (H-bond and dispersion effect between phenolic ring and π electrons). The overall PNP adsorption process was exothermic and spontaneous in nature according to thermodynamics parameters (free energy (ΔGo), enthalpy (ΔHo), and entropy (ΔSo)). We demonstrate that functionalization of CMK-3 with gold is possible (qm value for DBT: 15.33 mg/g and for CA: 13.00 mg/g). The adsorption capacity for As (V) on SBA-16- SO3H reaches 92.63 mg/g. The high removal of As equilibrium time of 90 minutes can be explained in terms of a strong electrostatic attraction that occurred between the SO3H and As. Maximum absorption capacity was 92.63 mg/g for As(V) was and 13.00 mg/g for Cu(II).
Original Research Paper
Carlos A Malca Reyes; Ermides Chavez Baldovino; Marielys Torres Diaz; Lisby F Santiago-Pagan; Peter Feng; Claudia P Ruiz-Diaz; Carlos Toledo-Hernandez; Kai Griebenow; Liz M. Diaz Vazquez
Abstract
The environmental fate and biological effects of nanomaterials in marine ecosystems are of increasing concern, yet monitoring techniques remain limited. This study explores alternative methods to evaluate the influence of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) on corals using Gorgonia ventalina as a model organism. ...
Read More
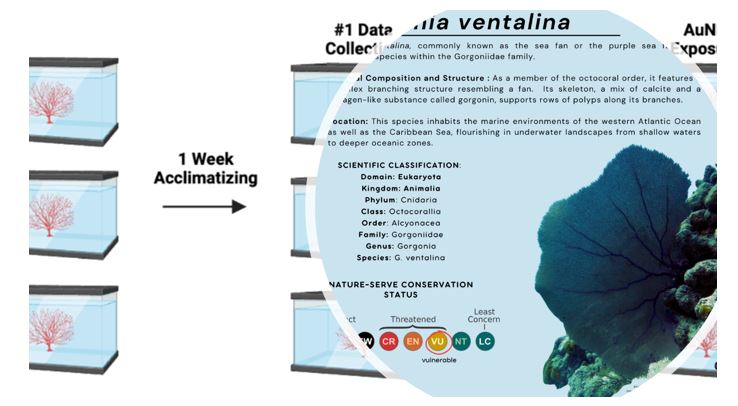
The environmental fate and biological effects of nanomaterials in marine ecosystems are of increasing concern, yet monitoring techniques remain limited. This study explores alternative methods to evaluate the influence of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) on corals using Gorgonia ventalina as a model organism. Through energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDAX), we traced AuNP accumulation within coral tissues. Raman spectroscopy revealed an elevation in polyene content, signifying a stress response attributable to nanoparticle exposure. Furthermore, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy demonstrated a reduction in calcium levels, while the Bradford assay indicated a decrease in protein concentration, suggesting a disruption in the calcification process vital to coral health. These findings highlight the utility of these alternative analytical techniques in providing comprehensive insights into the effects of nanomaterials on corals. The integration of these methods offers a more robust framework for environmental monitoring, with the potential to inform conservation strategies for marine ecosystems amid growing nanoparticle usegoogle is broken
Original Research Paper
Reza Torkamani; Bagher Aslibeiki; Masih Darbandi; Hamid Naghshara
Abstract
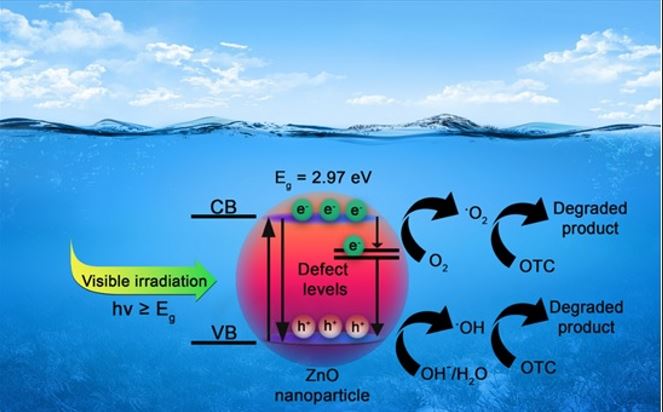
The toxicity of oxytetracycline (OTC) antibiotic remains in the environment and threatens the life of living things. In this research, two series of ZnO nanoparticle catalysts with different particle sizes were prepared.. The structural and optical characteristics of the samples were analyzed and the ...
Read More
The toxicity of oxytetracycline (OTC) antibiotic remains in the environment and threatens the life of living things. In this research, two series of ZnO nanoparticle catalysts with different particle sizes were prepared.. The structural and optical characteristics of the samples were analyzed and the photocatalytic degradation of OTC was investigated under a 100 W visible light irradiation. The samples prepared using zinc nitrate and zinc acetate showed different photocatalytic performance. The catalysts prepared at lower calcination temperatures show higher photocatalytic performance due to the active surface of the particles. The intensity of the peaks in the XRD patterns of samples also increases with increasing calcination temperature, which confirms the increase in the size of the nanoparticles. The decrease in particle size with increasing calcination temperature was confirmed by FESEM images. On the other hand, the band gap energy was reduced by decreasing the calcination temperature, which increases the performance of the photocatalytic activity. The 27 nm ZnO nanoparticles prepared using zinc nitrate showed 100 % degradation efficiency. As a result, we reached the maximum performance of pure ZnO by only controlling the size and morphology, without making nanocomposite or doping different elements.
google is broken
Original Research Paper
Asadollah Mohammadi; Parisa Abedi; Mohammad Reza Gholami
Abstract
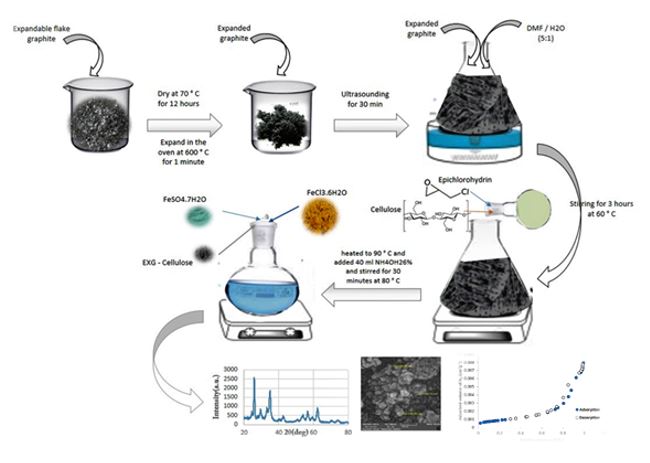
In this study, a new magnetic nanoadsorbent (denoted as Fe3O4/EXG/Cellulose) was synthesized using expanded graphite (EXG), microcrystalline cellulose and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The Fe3O4/EXG/Cellulose was used as an effective nanoadsorbent for the removal of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and malachite green ...
Read More
In this study, a new magnetic nanoadsorbent (denoted as Fe3O4/EXG/Cellulose) was synthesized using expanded graphite (EXG), microcrystalline cellulose and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The Fe3O4/EXG/Cellulose was used as an effective nanoadsorbent for the removal of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and malachite green (MG) from aqueous solutions using batch process. The Fe3O4/EXG/Cellulose was fully characterized by the Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses. Based on the BET analysis, an improved surface area from 10.32 to 71.86 m2 g–1 was achieved after the modification of expanded graphite using microcrystalline cellulose. The adsorption capacities for the MG dye and SMX drug were determined to be 109.9 and 3.9 mg/g, respectively. In addition, the adsorption process of SMX and MG by the Fe3O4/EXG/Cellulose was studied with isotherm and kinetic models. The results indicate the adsorption of SMX and MG by nanocomposite better described with pseudo-second-order kinetic. In addition, Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models well describe the adsorption of MG and SMX using Fe3O4/EXG/Cellulose, respectively. Furthermore, Fe3O4/EXG/Cellulose can be easily recycled and reused for over 5 times and keeps a high level of adsorption efficiency.
Original Research Paper
Geetanjali Lohiya; Anshu Tamta; Bhuwan Chandra; Narain Datt Kandpal; Rajendra Joshi
Abstract
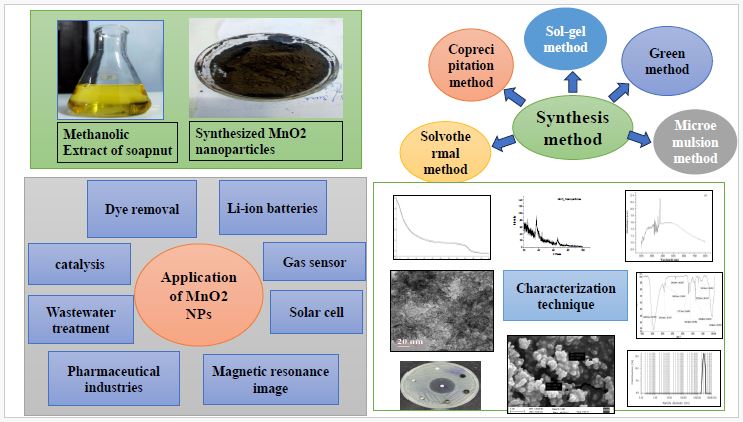
Nanoparticles of manganese oxide have been synthesized by a green chemistry approach using manganese chloride (MnCl2.2H2O), potassium permanganate (KMnO4), and methanolic extract of Sapindus mukorossi (reetha). In this study, we report here a simple ecofriendly green route to synthesize MnO2 nanoparticles. ...
Read More
Nanoparticles of manganese oxide have been synthesized by a green chemistry approach using manganese chloride (MnCl2.2H2O), potassium permanganate (KMnO4), and methanolic extract of Sapindus mukorossi (reetha). In this study, we report here a simple ecofriendly green route to synthesize MnO2 nanoparticles. Manganese oxide nanoparticles were characterized by Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR), UV-Vis spectral analysis, High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscope (HRTEM), and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). The surface morphology showed that the MnO2 nanoparticles were uniformly dispersed. The average particle size was found 16 nm obtained by X-ray Diffraction (XRD), analysis. To find particle size DLS analysis has been done. The thermal stability of the nanoparticles with the temperature increase has been determined by Thermo-gravimetric Analysis (TGA) measurement. The synthesized manganese oxide nanoparticles were screened for antibacterial activities on gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, and gram negative bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli. The results of the antibacterial study suggest that the manganese oxide nanoparticles can be useful for effective growth inhibitors in microorganisms with applications to medical devices and antimicrobial-controlled systems. The order of the reactivity towards zone of inhibition of microorganisms observed in the order of Escherichia coli (9mm) > Pseudomonas aeruginosa (8.3mm) > Bacillus subtilis (7.3mm) > Staphylococcus aureus (5.3mm).
Review Paper
Tahereh Raiesi Ardali; Leila Soleimanpour; Leila Mamani; Mostafa Chorom
Abstract
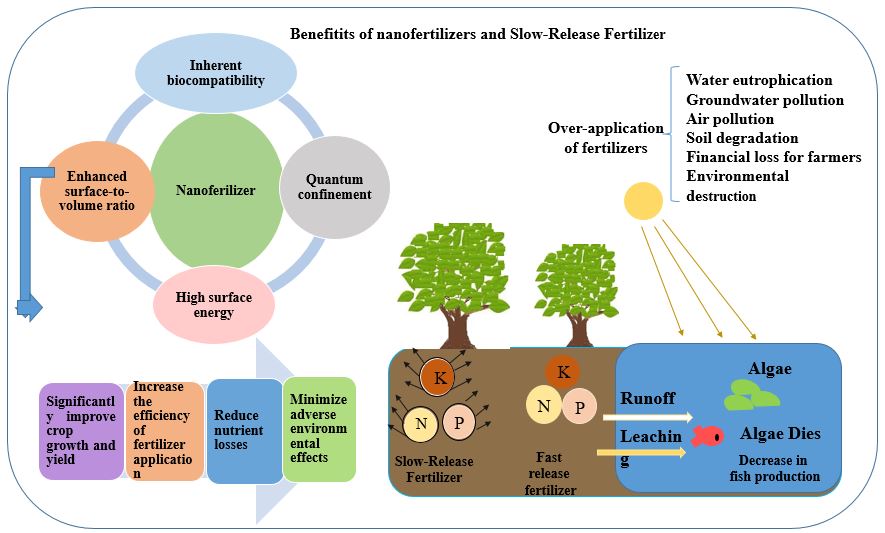
Nanofertilizers offer opportunities for the development of new types of fertilizers. In this study, we focused on the different types of nano fertilizers that enhance plant growth and reduce harmful environmental effects. Nanofertilizers, especially when using new technologies in fertilizer products ...
Read More
Nanofertilizers offer opportunities for the development of new types of fertilizers. In this study, we focused on the different types of nano fertilizers that enhance plant growth and reduce harmful environmental effects. Nanofertilizers, especially when using new technologies in fertilizer products such as nano-encapsulation and controlled release of nutrients, can increase plant nutrient uptake, enhance fertilizer efficiency, improve soil quality, and decrease environmental effects. This article discusses different types of nanofertilizers, including macronutrient nanofertilizers, micronutrient beneficial element nanofertilizers, novel technologies for fertilizer nutrients, and materials used in fertilizers. This article reviews literature using natural and synthetic coatings for the slow release of urea. The potential of environmentally friendly natural coatings compared to synthetic coatings has also been investigated. These composites, with excellent slow-release properties and non-toxicity to soil and environment, could be used in horticultural applications for higher agricultural production efficiency. Finally, this review suggests that nano fertilizers can increase crop production and reduce plant nutrient losses. Although the use of nanoparticles has many advantages, entering the global market requires more studies to investigate their comprehensive effects on the environment.
), scientific journal published in association with Iran Nanotechnology Initiative Council (INIC) and Iranian Environmental Mutagen Society, devoted to the dissemination of original research articles and topical reviews on water and environmental nanotechnology and related issues such as nano-safety, monitoring and management studies. Mutational bases of the effects of nanotechnology on environment also fall within the scope of the journal. The journal is intended to provide state-of-the-art expositions of latest advances by theoretical, numerical and experimental studies across the spectrum of the field, from scientific enquiries to practical applications. The journal can cover nanoscale science and technology relevant to water and environment, risk assessment activities and regulatory policies on issues of environmental and human health and nano-focused water and environmental research as well as environmental mutation area. This journal intends to be interests of international scholars, researchers, practitioners and academic members, industrial and governmental sectors. This journal is open access and all available content and materials on it are available for free under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. (CC-BY 4.0).